Which IDC Flat Ribbon Cable Is Right for You?
Release time:
2025-07-26
China IDC flat ribbon cables supplier
Which IDC Flat Ribbon Cable Is Right for You?
For most people who want a cable that works well and lasts, an IDC Flat ribbon cable is a great pick. This cable is used in lots of electronics, like computers and cars. It lets you make quick and safe connections. You do not need to strip wires or use solder.
IDC Flat ribbon cables help link parts inside computers, like hard drives and screens. They are also important in car wiring harnesses. Every project is different. You should think about your device, where you will use it, and what kind of connection you need before picking a cable.
Key Takeaways
- Make sure the cable pitch and number of conductors match your device and connector. This helps the cable fit safely and properly.
- Pick insulation and wire gauge based on where and how you will use the cable. Think about heat, bending, or power needs.
- Trusted brands last longer and are safer. They work better, especially for important or long-term projects.
- Flexible and specialty cables are best for tight spaces or moving parts. Standard cables work well for most general uses.
- Do not make mistakes like using the wrong pitch, poor strain relief, or mixing brands. This helps keep your connections reliable.
Choosing an IDC Flat Ribbon Cable
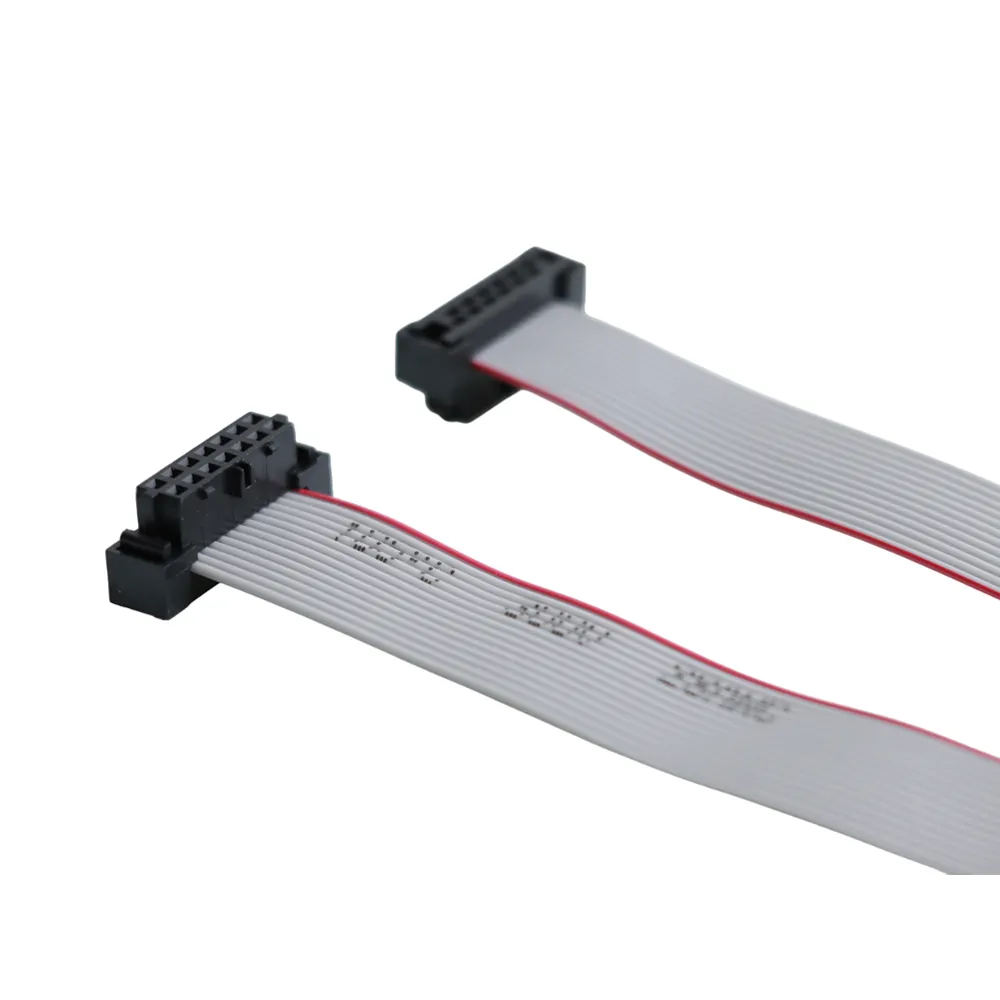

Key Factors
When you pick an IDC Flat ribbon cable, you need to know what makes it work well. Pitch is the space between each conductor. This is very important. Some common pitches are 0.5mm, 1mm, 1.25mm, and 2mm. The pitch of your cable must match the connector’s pitch. If you use a 2.54 mm pitch cable with a 1.27 mm connector, it will not fit. The pitch must line up for a safe connection.
The number of conductors in the cable is also important. IDC Flat ribbon cables can have 2 to 50 conductors. More conductors mean you can send more signals or power. This helps in devices that are complex or crowded. The number of conductors changes how flexible the cable is. It also affects how well the cable works with electricity.
Flexibility is another thing to think about. Some cables use stranded wires and special covers. This lets them bend easily and fit in small spaces. Flexible cables are good for robots, medical tools, and other places where the cable must move or fit tightly. How long the cable lasts depends on how flexible it is, especially if it moves a lot.
Insulation keeps the wires inside safe. Materials like butyl polymer and silicone protect against heat, cold, chemicals, and damage. Some cables use high-temperature PBT or low-smoke, halogen-free materials. These help stop fires and meet safety rules. These features make the cable good for tough places like factories or outside.
Certifications show the cable is safe and good quality. Many projects in factories or cars need UL, ISO, or RoHS certifications. These rules make sure the cable can handle high voltage, resist fire, and does not have dangerous stuff.
Tip: Look for a red stripe or color on the cable edge. This helps you connect it the right way.
Specifications
You need to match the cable’s details to your project. The wire gauge, often 28 AWG, must carry enough current and be strong enough. Some projects need a different gauge for more power or more bending. Where you use the cable, like in a factory, car, or home project, will help you pick the right insulation, flexibility, and certifications.
The type of IDC Flat ribbon cable matters too. Standard cables work for most jobs. Shielded, twisted, or bonded cables give extra protection from noise or damage. Folded cables save space in small places.
The cable and connector must fit together. The pitch and number of conductors must match the connector. The size, shape, and direction of the connector also matter for a good fit.
Ribbon and flat cables are not always the same. Ribbon cables have wires side by side in a flat strip. This makes them easy to organize and connect. Flat cables may look different and can be more flexible or strong. A-type and B-type mean different wiring patterns. These must match what your device needs.
When you pick an IDC Flat ribbon cable, use this checklist:
- Make sure the pitch and number of conductors match your connector and device.
- Pick the right insulation for where you will use the cable.
- Choose the right wire gauge for power and bending.
- Check for certifications if your project needs them.
- Decide if you need a standard, shielded, or flexible cable.
If you think about these things, you can find a cable that works well for your project and will last.
IDC Flat Ribbon Cable Brands
Leading Brands
Many engineers pick famous brands for their IDC Flat ribbon cable needs. These brands give strong performance, safety, and dependability.
- Cicoil uses special Flexx-Sil™ jacket technology. Their cables work in very hot or cold places, from -65°C to +260°C. They do not get damaged by chemicals or water. This makes them good for tough or clean places. Cicoil cables can bend, fold, or twist and still work well. They meet strict certifications like UL, CSA, CE, RoHS, and ISO 9001. Cicoil cables have even gone to space.
- Molex makes Temp-Flex cables for hot and rough places. These cables do not wear out easily and resist chemicals. They are good for machines and places where cables get pulled or pushed.
- 3M has foldable ribbon cables with steady impedance. These cables move data fast and have connectors with gold on them. 3M cables are used in computers and communication devices.
- TE Connectivity makes cables with strong insulation and high current ratings. Their cables work well in printed circuit boards and other electronics.
- Amphenol sells many types of IDC Flat ribbon cables. Their cables are used in many industries, but less is known about their special features.
Note: Top brands usually cost more, but they last longer and work better.
Generic Options
Generic brands like Antrader, Sourcing Map, and Newhaven Display are cheaper. These cables are good for simple jobs or quick fixes. But people say generic cables have more quality problems.
- Sometimes the connection does not work because of bad IDC joints or contacts.
- Problems can happen if connectors are dirty or tools are not good.
- Some cables break because they do not have strain relief.
- About 5% of these cables fail, even in safe places.
Tip: For important or long-lasting projects, use trusted brands. Use generic cables only for easy or short-term jobs.
Comparison
Specs Overview
You need to check the details to pick the right cable. Each brand has different specs for different jobs. The table below shows how top brands are different in key ways:
Note: Cables that cost more often have better insulation. They are tougher and can handle more heat, cold, or chemicals.
Applications
IDC Flat ribbon cable was first used in big computers. Now, these cables are in many things. Printers, computers, and drives use them for fast and tidy links. The number of conductors depends on what the device needs. For example, floppy drives use a 34-conductor cable. Hard drives use a 40-conductor cable.
Pitch size is important for small spaces. Small devices use cables with a pitch as tiny as 0.33 mm. Color stripes and edge marks make cables easy to tell apart. Twisted pair and hybrid cables help cut down noise. They also let medical and factory machines send mixed signals.
Some cables have extra features. Flexible cables fit in tight or moving spots. High-temperature insulation keeps cables safe in tough places. Ratings like IP55 or IP67 show if a cable keeps out dust and water. Strong cables last longer in factories or outside.
Tip: Always check that the cable’s specs match your device and where you will use it for the best results.
Recommendations
Prototyping & DIY
Many hobbyists and engineers use IDC Flat ribbon cable with a 0.1 inch pitch for building and testing electronics. This pitch fits standard connectors and breadboards. It makes putting things together easy and dependable. Users do not have to solder, so they save time and make fewer mistakes. These cables are good for projects like LED panels, Raspberry Pi GPIO links, and eurorack synths.
For the best results, people should pick cables and connectors from trusted brands. 3M has many flat ribbon cables, including twisted-pair and flat styles. Buying ready-made cables or kits from good sellers helps avoid bad parts. A 100-mil 6-pin 2x3 IDC flat cable, used with devices like ATMEL-ICE, is a common choice for most building needs.
Tip: You can make your own cables for personal projects. But using good parts from known brands gives better results.
Industrial Use
Factories need cables that can handle rough places. Users must check that the cable pitch matches the connector or PCB header. The wire gauge should fit the connector’s range to stop loose connections or damage. Environmental sealing, like IP67 or IP55, keeps out water, dust, and chemicals.
Cables with silicon jackets, like EZ-Flexx flat cables, work well in hot areas. These cables can handle temperatures from -65°C to 260°C. They also stand up to shaking, hits, and strong chemicals. M12 IDC connectors are another good pick for factories. They do not shake loose, keep out water, and are easy to install without tools. These features make them great for sensor and actuator links in machines.
- Match cable pitch and wire gauge to the job.
- Use cables that resist heat and fire.
- Pick cables with strain relief for use with lots of shaking.
- Choose cables with the right ratings for dust and water.
- Pick connectors that are easy to put in at the job site.
Note: Good cables help stop breakdowns and repairs in factories.
Specialty Needs
Some projects need cables with special features. High-density layouts, like in cameras or medical tools, need cables that carry many signals in a small space. Custom IDC Flat ribbon cable sets can be made for special designs. These cables may have double shielding, plenum ratings, or hybrid builds that mix power, data, and coaxial wires.
Cicoil’s very flexible cables use Flexx-Sil™ jackets. These cables work in very hot or cold places and resist scratches, chemicals, and sunlight. They can fix themselves and last a long time, even if bent a lot. Hybrid and intermittent-bonding ribbon cables bend more and offer special pin setups for board-to-board links.
- Pick strong, heavy-duty cables for tough places or when you need extra strength.
- Use very flexible cables for robots, planes, or medical tools where cables must bend or twist a lot.
- Choose custom or hybrid cables for projects with special space, signal, or place needs.
- Look for certifications like ISO 9001, UL, and RoHS to make sure the cable is good quality.
Callout: You can get custom cables for projects that need special shapes, materials, or safety marks.
Buying Tips
Selection Guide
Choosing the right IDC Flat ribbon cable starts with understanding the project’s needs. Buyers should follow a step-by-step process to match cable features to their requirements:
- Check the cable size and type. Make sure the connector forks and U-channels fit the cable. All wires in one connector must have the same size.
- Think about storage. If the project uses many connector sizes, buyers need to keep different ribbon cable sizes in stock.
- Look at the cable path. Ribbon cables bend less than single wires. Plan the route to avoid sharp turns or tight spaces.
- Review connector options and current needs. IDC connectors come in fewer sizes and may not work for high current or harsh environments.
- Gather all project details. Sometimes, the project needs more than the client expects.
- Use design tools to create a digital model of the cable assembly.
- Build and test prototypes. Check for strength, safety, and function.
- Test the cable in different conditions, like heat, bending, or saltwater.
- Start full production only after the design passes all tests.
Tip: Always use cables and connectors from the same brand for better fit and fewer problems.
Common Mistakes
Many buyers make simple errors when picking an IDC Flat ribbon cable. Avoiding these mistakes helps projects run smoothly:
- Using the wrong pitch. The connector, cable, and PCB header must match in pitch.
- Picking the wrong wire gauge. The wire must fit the connector to avoid loose or damaged links.
- Ignoring size and shape. Some projects need low-profile or right-angle connectors.
- Forgetting color codes and keying. These features help prevent assembly errors.
- Not checking cable length and routing. Short or poorly routed cables can fail early.
- Skipping strain relief. Without it, cables may break from bending or movement.
- Failing to test connections. Use continuity tests to make sure everything works.
- Mixing brands. Using connectors and cables from different brands can cause fit or reliability issues.
Note: Careful planning and checking each step can prevent most common problems.
Picking the right IDC Flat ribbon cable means you need to match the conductor count, pitch, and insulation to what you are using it for. Top brands work best in tough places, but generic cables are fine for easy jobs.
- Here are some important tips:
- Make sure the cable matches your device’s needs
- Think about if you need shielding or a certain temperature rating
- Check that the connector fits with your cable
You can ask manufacturers or suppliers for help if you need a special cable or have questions. Companies like Amphenol LTW and 3M have guides and can help you pick and install the right cable.
FAQ
What does "pitch" mean in IDC flat ribbon cables?
Pitch shows the distance between each wire in the cable. Most cables use pitches like 1.27 mm or 2.54 mm. The pitch must match the connector for a safe and proper fit.
Can users cut IDC flat ribbon cables to custom lengths?
Yes, users can cut these cables to the needed length. They should use sharp scissors or a cable cutter. After cutting, users must attach a new IDC connector for a secure connection.
How do users know which side is pin 1 on a ribbon cable?
Most cables have a red stripe or colored edge. This stripe marks pin 1. Users should match this side with pin 1 on the connector or device.
Are IDC flat ribbon cables reusable?
Some IDC connectors allow reuse, but most work best for one-time use. Reusing connectors may cause weak connections. For best results, users should use a new connector each time.






